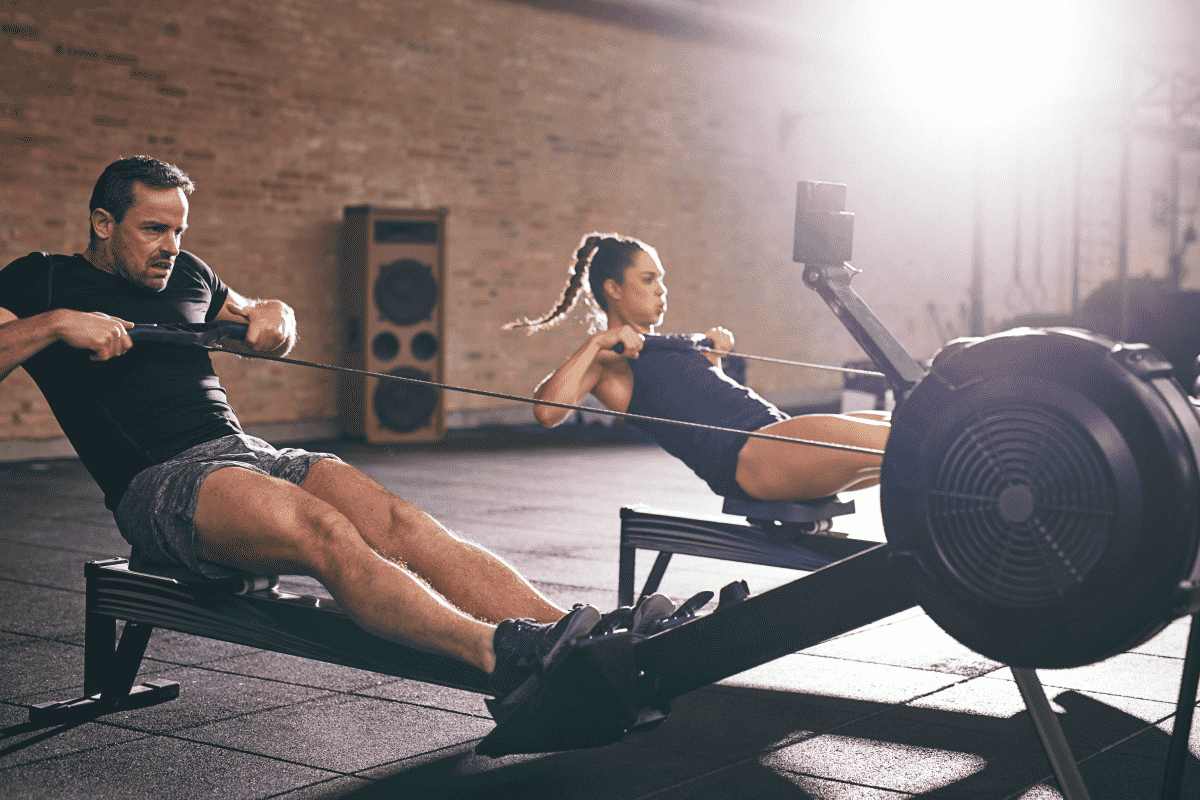
Rowing, often overshadowed by flashier gym equipment, can help unlock a powerful, sculpted physique.
Unlike the deceptive simplicity of its motion, rowing is a complex, full-body workout that challenges and builds muscle in ways many workouts can’t match. Let's dive into why the rowing machine, or the hydro rower, is not just another cardio device but a cornerstone for strength training.

How to Use a Rowing Machine
Mastering the rowing machine involves a few critical steps for an effective and safe workout:
- Setting Up: Secure your feet in the straps and set the damper between 3 and 5 for a realistic rowing feel.
- The Catch: Start with knees bent, shins vertical, leaning slightly forward, arms extended, holding the handle.
- The Drive: Push through your feet to extend your legs, lean back slightly, and pull the handle to your lower ribs.
- The Finish: Legs extended, body leaned back, handle at your lower ribs, shoulders down, elbows in.
- The Recovery: Extend arms, lean forward from the hips, and bend knees to return to the catch position.
Rowing: Tips and Tricks
To maintain an effective rowing workout, keep your movements smooth and consistent. Prioritizing form over speed is essential, especially in the beginning, to reduce the risk of injury and ensure you're working the intended muscle groups efficiently.
Control your breathing by exhaling forcefully on the drive as you exert force and inhaling during the recovery phase to prepare for the next stroke. These simple adjustments can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your rowing sessions.
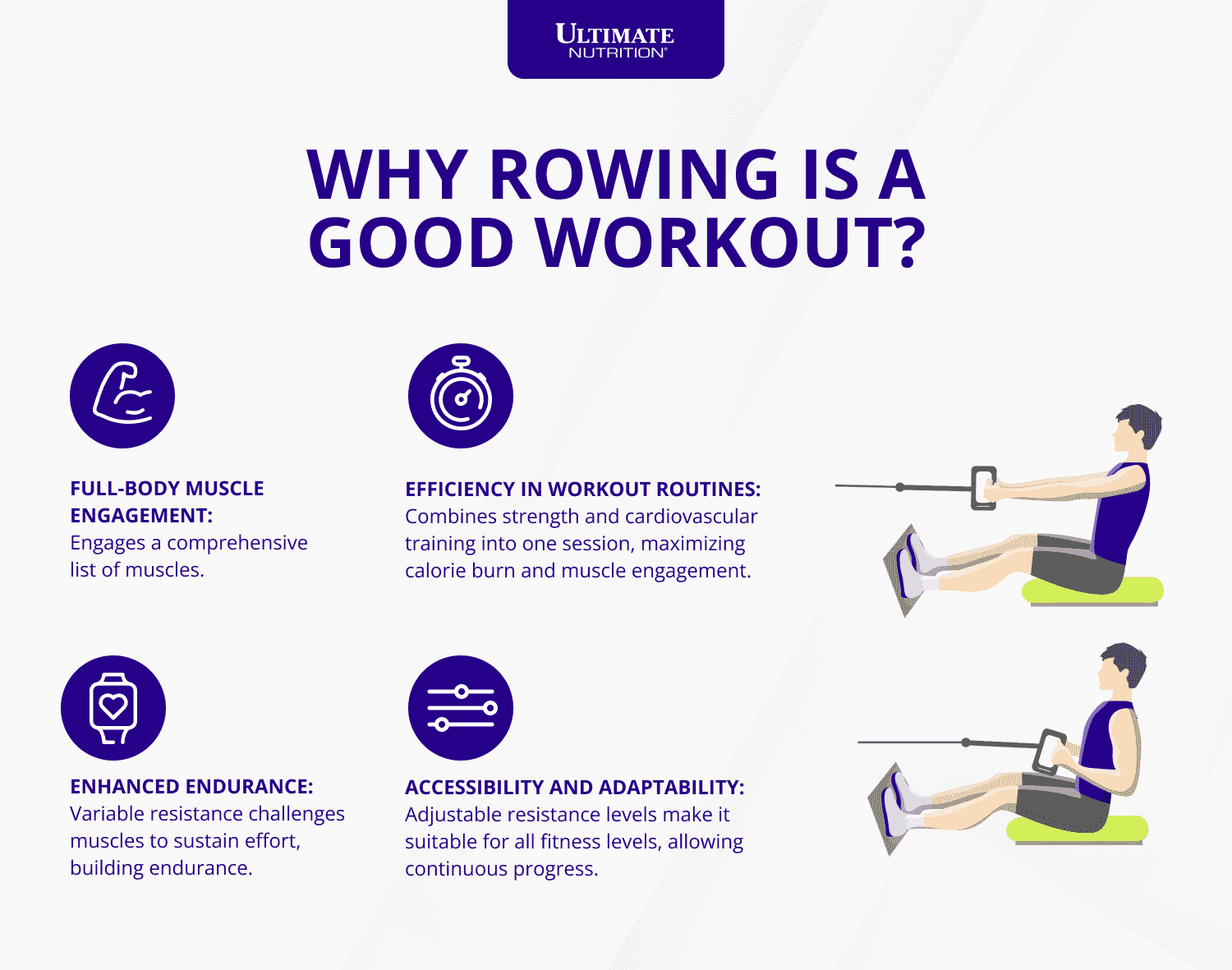
Why Rowing is a Good Workout
Rowing stands out as an exceptionally effective workout for several compelling reasons.
Rowing Muscles Worked
One of rowing's most significant advantages is its ability to engage a comprehensive list of muscles throughout the body, making every stroke a full-body workout.
The major muscle groups worked include:
- Legs: The quads and hamstrings primarily power the drive phase, along with the calves for stabilization and support.
- Core: The abdominals and lower back muscles are constantly engaged to maintain proper posture and transfer power between the lower and upper body.
- Upper Back: The latissimus dorsi muscles are key players in the pulling phase, essential for the powerful finish of each stroke.
- Shoulders and Arms: Deltoids, biceps, and triceps work together to control the handle during the drive and recovery phases, ensuring a smooth motion.
- Glutes: Activated during the drive to extend the hips and contribute to the powerful leg drive that is central to the stroke.
Enhanced Endurance
The repetitive nature of rowing with variable resistance challenges muscles to sustain effort over time, effectively building endurance.
This type of endurance benefits overall fitness, supporting longer, more intense training sessions across all workouts, not just rowing.
Efficiency in Workout Routines
Rowing is time-efficient; it combines strength and cardiovascular training into one session.
This dual approach maximizes calorie burn and muscle engagement within a shorter time frame, which is ideal for those with busy schedules seeking comprehensive workout solutions.
Accessibility and Adaptability
The rowing machine's adjustable resistance makes it accessible for beginners while offering challenging workouts for advanced athletes.
This adaptability means users can continuously progress, increasing resistance as their fitness improves, ensuring ongoing muscle and strength development.

Best Rowing Machine Exercises
Diversifying your rowing routine with specific exercises can enhance strength and cardiovascular endurance. Here are some of the best rowing machine exercises:
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) Row
To perform HIIT training, start with a moderate pace warm-up for 5-10 minutes, then alternate between 30 seconds of maximum effort rowing and 1-2 minutes of low-intensity recovery rowing.
This contrast enhances endurance and boosts metabolic rate.
Pyramid Power Rows
Pyramid Power Rows gradually increase and then decrease the intensity and duration of your rowing intervals, mimicking the shape of a pyramid.
Begin with a 1-minute row at a high intensity, followed by 1 minute of rest, then increase the rowing interval by 1 minute each time until you reach a peak (usually 4-5 minutes) before reversing the pattern.
This method improves stamina and strength by challenging your body's ability to recover and adapt to changing intensities.
Endurance Rows
The Endurance Row is key for those looking to build stamina and muscular endurance.
Settle into a consistent, moderate pace and row for an extended period, typically 20-30 minutes or more. This exercise encourages muscular and cardiovascular efficiency, training your body to sustain effort over time.
Sprint Rows
Sprint Rows focus on short, explosive efforts to build power and speed. After warming up, row as hard as you can for 20-30 seconds, then take a full minute or two of rest or gentle rowing to recover. Repeat for 5-10 rounds.
These sprints are excellent for increasing your stroke rate and power, translating to improved performance on and off the rowing machine.

Find Your Power With Ultimate Nutrition
If you’re putting the time into rowing, ensure you get the most out of it.
At Ultimate Nutrition, we’ll fuel you with the latest and greatest protein powders. Use our Performance and Recovery powders to fuel your most intense sessions and our Weight Loss mixes to help tone down your body.
When you’re ready to add more workouts, explore our exercises and training blog. We’ll keep you stocked up on the critical information you need to keep your body charged.
It’s row time!
The information provided in our articles are meant for informational and educational purposes exclusively and should not be considered as medical advice. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting a new nutritional product and/or making significant changes to your diet and/or starting a new exercise regime. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, and/or prevent disease.







